Manufacturers constantly face the challenge of balancing speed, quality and cost. In many plants, production teams rely on manual spreadsheets or siloed systems, which creates inefficiencies and leads to downtime. By investing in a manufacturing ERP implementation, organizations can connect planning, operations and maintenance in a single system.
A modern ERP for manufacturing provides visibility into orders, materials and machine performance. It enables managers to optimize production scheduling, minimize disruptions and reduce downtime. This blog explores how to implement ERP effectively, with a focus on production scheduling, predictive maintenance and long-term success.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhy Manufacturing ERP Implementation Matters
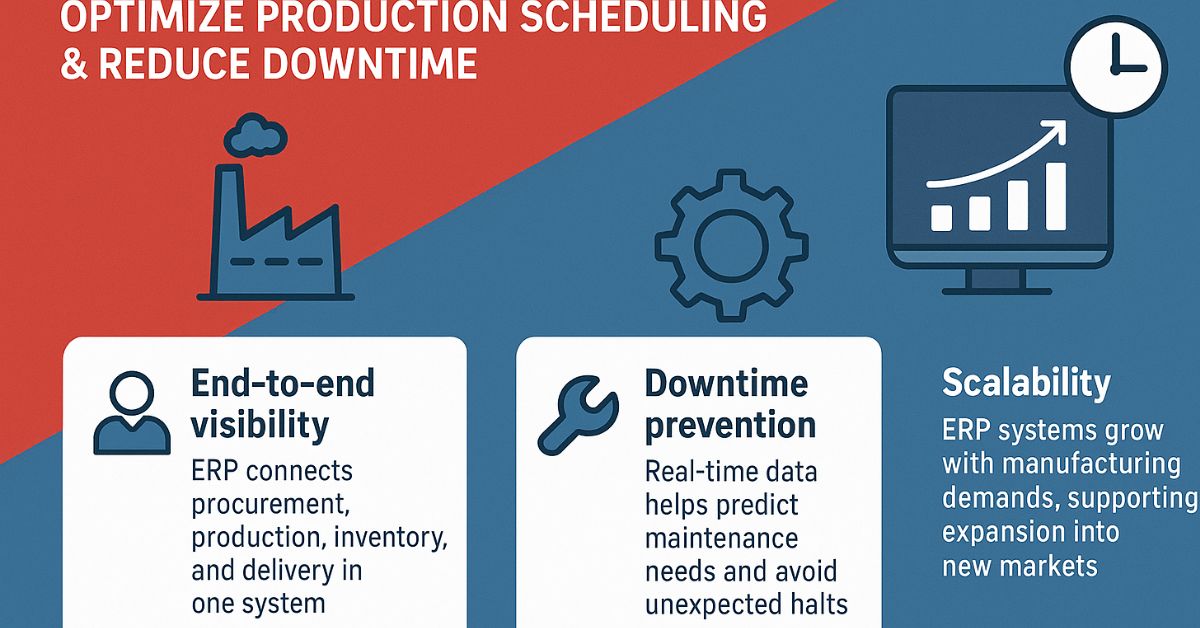
A successful manufacturing ERP implementation delivers value beyond finance or reporting. It directly impacts shop floor performance, customer delivery and asset utilization.
1- Centralized planning: An ERP system for manufacturing consolidates data from sales, procurement and production, giving planners one version of the truth.
2- Stronger scheduling discipline: Automated scheduling aligns labor, materials and capacity, replacing error-prone manual methods.
3- Reduced downtime: Predictive maintenance tools in ERP systems prevent unexpected equipment failures.
4- Scalability: ERP grows with the business, supporting multiple plants, geographies and new product lines.
By standardizing processes and improving visibility, ERP transforms the manufacturing operation into a more predictable and efficient system.
Optimizing Production Scheduling with ERP
Production scheduling is one of the most complex tasks in the manufacturing industry. Without the right tools, companies face bottlenecks, missed delivery dates and excess work in progress. A production scheduling ERP module helps managers align resources, orders and capacity in real time.
1- Finite capacity planning: The ERP enforces realistic limits, ensuring that no machine or team is overbooked. This prevents late orders and costly overtime.
2- Dynamic rescheduling: A strong ERP for manufacturing adapts instantly when demand shifts, materials are delayed or machines go down.
3- Material-driven scheduling: By integrating procurement and inventory, production starts only when raw materials are available. This avoids idle labor and machines.
4- On-time delivery improvements: With optimized scheduling, manufacturers can consistently meet customer commitments.
Effective manufacturing ERP implementation best practices emphasize aligning scheduling with supply chain data. This integration reduces uncertainty and helps manufacturers achieve higher efficiency.
Reducing Downtime Through ERP Tools
Downtime is one of the biggest threats to productivity and profitability. Unexpected breakdowns halt production, waste resources and delay shipments. ERP systems address downtime with predictive tools and integrated maintenance functions.
1- Predictive maintenance: A modern ERP system for predictive maintenance in manufacturing connects with IoT devices and machine sensors. It alerts teams to potential issues before breakdowns occur.
2- Planned maintenance windows: ERP schedules maintenance during low-demand periods, ensuring that servicing does not affect order fulfillment.
3- Resource readiness: The system ensures spare parts, technicians and tools are available at the right time. This prevents delays once maintenance begins.
4- Downtime analytics: ERP tracks every incident, helping managers understand root causes and implement preventive measures.
By adopting ERP implementation in manufacturing industry, businesses shift from reactive to proactive maintenance. This directly reduces downtime, increases equipment availability and boosts return on investment.
Key Phases of a Manufacturing ERP Implementation
A structured roadmap ensures that the ERP project achieves its goals. From planning to post-go-live, each phase of a manufacturing ERP implementation requires disciplined execution.
1- Planning and requirement gathering: Define goals such as reducing downtime, optimizing production scheduling or improving on-time delivery.
2- System configuration: Customize modules for bill of materials, routings and shop floor control. Configure ERP benefits for manufacturers such as traceability and compliance.
3- Testing and training: Run end-to-end tests of production scheduling, order execution and maintenance workflows. Train employees in sandbox environments.
4- Go-live and monitoring: Roll out in phases and monitor key metrics like schedule attainment, machine uptime and order cycle times.
Following this roadmap minimizes disruption and accelerates value capture from the ERP system.
Data Accuracy and Master Records
ERP systems deliver accurate scheduling and maintenance insights only when the data is clean. Poor data quality creates delays, incorrect schedules and unreliable downtime reporting.
1- Clean master data before migration: Standardize part numbers, units of measure and routing steps.
2- Define ownership: Assign responsibility for materials, work centers and bills of materials to ensure accountability.
3- Enforce governance: Use ERP workflows to prevent incomplete or incorrect records from entering the system.
4- Continuous audits: Periodically review data to catch errors and ensure accuracy over time.
These steps support optimizing production scheduling with ERP and strengthen decision-making on the shop floor.
Change Management and User Adoption
ERP systems succeed when employees adopt them. A manufacturing ERP implementation must include structured change management to prepare teams for new processes.
1- Role-based training: Provide hands-on sessions tailored for planners, supervisors, operators and maintenance staff.
2- Practical learning environments: Let users practice in sandbox environments before go-live.
3- Clear communication: Explain benefits such as fewer errors, less downtime and easier reporting.
4- Super users and champions: Build a network of trained employees who can support peers during rollout.
Change management ensures that ERP is not seen as an IT project but as a tool that makes daily tasks easier and more reliable.
Measuring Success and ROI
Decision-makers, especially CFOs and operations leaders, must measure whether ERP investments deliver value. Tracking the right KPIs ensures accountability.
1- Overall equipment effectiveness (OEE): Measure uptime, performance and quality improvements.
2- Mean time between failure (MTBF): Confirm that machines last longer between breakdowns.
3- Schedule attainment: Track whether production orders finish on time as planned by the ERP.
4- Inventory turns: Validate whether integration with scheduling reduces excess work in progress.
These KPIs prove the ERP benefits for manufacturers and help justify future system expansion.
Best Practices for Long-Term Success
Sustained benefits come from adopting best practices. Companies that treat ERP as a continuous improvement platform gain more than those who see it as a one-time project.
1- Start with a pilot: Roll out ERP on one product line before scaling.
2- Minimize custom code: Use standard ERP configurations to reduce future upgrade issues.
3- Integrate IoT early: Link machine sensors and shop floor devices to maximize real-time insights.
4- Iterate continuously: Use ERP analytics to refine scheduling, improve maintenance and cut downtime over time.
Following steps for successful manufacturing ERP implementation positions companies for ongoing efficiency gains.
Conclusion
Manufacturers who invest in manufacturing ERP implementation gain measurable improvements in production scheduling, downtime reduction and overall efficiency. By connecting scheduling with inventory, labor and equipment data, ERP provides real-time control and better visibility. By integrating predictive maintenance, ERP reduces unplanned downtime and improves asset utilization.
When implemented with clean data, strong change management and a structured roadmap, ERP systems deliver long-term competitive advantage. For manufacturers, this is not just a software investment. It is a foundation for operational excellence, improved customer satisfaction and sustainable growth.